Starlink’s Entry into Uganda
Masters Of Sites
21/04/2025
Understand Starlink Techonology
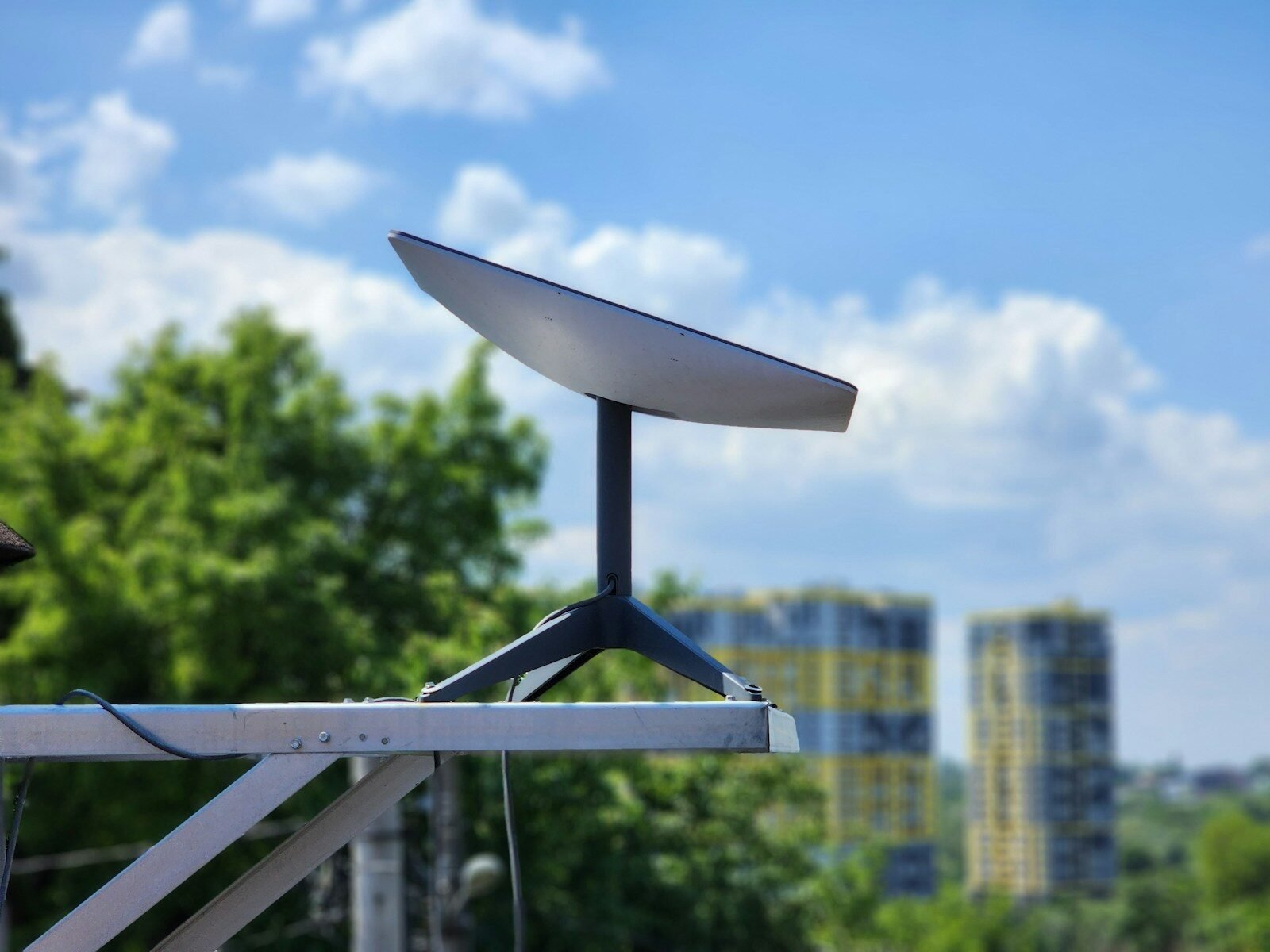

Introduction
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation launched by SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk in 2002. The project aims to provide high-speed, low-latency internet access globally, particularly in underserved and remote areas where traditional broadband is lacking. Since its beta launch in late 2020, Starlink has deployed thousands of satellites in low Earth orbit, enabling users to connect via specialized terminals or “dishes.” Offering download speeds between 50 Mbps and 200 Mbps with latency of 20-40 milliseconds, Starlink is revolutionizing global connectivity and working to bridge the digital divide across diverse regions.
Starlink’s entry into the Ugandan market represents a significant shift in how internet connectivity can evolve in the country, especially for rural regions where traditional infrastructure has lagged. As the world increasingly embraces digital transformation, Uganda finds itself at a crossroads—where satellite-based broadband could redefine who gets connected, how fast, and at what cost.
Here’s a deeper look into how it all works and the implications for Uganda’s digital landscape, ISP dynamics, and the everyday internet user.
How Starlink Connectivity Works
Starlink uses a constellation of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites to deliver high-speed internet. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the system:
Satellite Network
Starlink operates thousands of satellites orbiting between 340 km and 1,200 km above Earth. This proximity dramatically reduces latency compared to traditional geostationary satellites, enabling smoother real-time experiences like video conferencing and online gaming.User Terminals
Users access the internet through a small satellite dish—called a user terminal—which automatically aligns with the satellite network. The device is plug-and-play, designed for ease of use without needing complex installation.Ground Stations
Starlink satellites communicate with Earth-based ground stations that connect to the global internet. The more ground stations in a country or region, the more stable and expansive the service becomes.Signal Transmission
Data is transmitted from the user’s dish to a satellite, relayed to a ground station, and sent back—completing a full cycle in milliseconds. This system ensures fast, reliable internet access even in places where fiber or mobile networks are unavailable.
Potential Impact on Uganda
Starlink’s arrival brings both opportunities and challenges. Here’s a breakdown of the most likely effects:
✅ Pros:
Nationwide Reach
Starlink can reach places where fiber optics and cellular towers are either unavailable or economically unfeasible. This could help bridge Uganda’s long-standing rural-urban digital divide.Improved Reliability
In areas with frequent internet or power outages, Starlink offers a resilient alternative or backup connectivity option, particularly valuable for schools, health centers, and remote businesses.Boosting Innovation & Inclusion
Reliable internet access fosters innovation. Entrepreneurs, developers, students, and researchers in remote areas could benefit from new digital opportunities, leveling the playing field.
⚠️ Cons:
Cost Barriers
Despite its benefits, Starlink’s initial hardware costs and monthly fees remain high for most Ugandans. Without subsidies or local pricing models, adoption may be limited to well-resourced individuals and institutions.Pressure on Local ISPs
Traditional ISPs may struggle to compete on performance or coverage. This could lead to market disruption, price wars, consolidation—or in a worst-case scenario, job losses within the local ISP ecosystem.Regulatory Complexity
Uganda’s regulators must now develop frameworks around satellite licensing, taxation, and frequency spectrum use. Without this, integration into the national telecommunications environment could become complicated or even contentious.
Key Questions and Considerations
As Starlink settles into Uganda, several critical questions arise:
Will local ISPs innovate or retreat?
Traditional providers may need to adopt hybrid models, improve customer service, or specialize in niche areas (e.g., urban fiber bundles or business-centric packages) to stay relevant.Can Starlink become truly affordable?
For mass adoption to occur, costs will need to align with local income levels. Could partnerships, local distributors, or subsidy programs be part of the solution?What should policymakers do?
Regulatory authorities will need to ensure fair competition while safeguarding consumer interests. This means creating policies that allow innovation without monopolizing the space.Will connectivity quality drop as usage increases?
Starlink’s network speed can decline when too many users connect to the same satellite beam. As adoption grows, user density management and satellite capacity expansion will become critical.
Conclusion
Starlink has the potential to redefine internet connectivity in Uganda, particularly in underserved and remote regions. Its presence could be a catalyst for digital inclusion, technological innovation, and economic growth. However, it’s not without challenges—ranging from affordability to regulatory oversight and market disruption.
The success of Starlink in Uganda will depend on collaboration between government, local ISPs, and the private sector. With the right strategies, this new chapter in internet access could usher in a more connected, inclusive future.
What Do You Think?
Is there potential for collaboration between Starlink and local ISPs, or will the market become increasingly competitive?
How can regulators balance innovation and fairness in this new era of connectivity?
Could Starlink be the answer to Uganda’s rural connectivity gap, or will it remain a premium service for a select few?
💬 Join the conversation in the comments or share this post with your network. Let’s discuss how we shape the future of internet access in Uganda!
Recent Post
-
 21 Apr 2025Starlink's Entry into Uganda
21 Apr 2025Starlink's Entry into Uganda -
 13 Dec 2024My WhatsApp is Hacked
13 Dec 2024My WhatsApp is Hacked -
 29 Oct 2024Choosing the Best Fibre Internet in Uganda
29 Oct 2024Choosing the Best Fibre Internet in Uganda -
 12 Sep 2024Starting Your Own WiFi Hotspot Business
12 Sep 2024Starting Your Own WiFi Hotspot Business -
 31 Jul 2024Overcoming Challenges for Businesses with Limited Security Resources
31 Jul 2024Overcoming Challenges for Businesses with Limited Security Resources -
 11 Apr 2024Unleashing Creativity: Finding the Best Website Company for Web Development and Design
11 Apr 2024Unleashing Creativity: Finding the Best Website Company for Web Development and Design -
 24 Mar 2024Exploring Cybersecurity and Its Career Paths
24 Mar 2024Exploring Cybersecurity and Its Career Paths -
 16 Mar 2024The Art of AI to Maximize Business Success
16 Mar 2024The Art of AI to Maximize Business Success
Categories
Grow Your Business Today
Empower your business growth with our innovative solutions and strategic expertise. Start expanding your success today with our comprehensive services.

